California is known for its stringent safety and health regulations, which often exceed those of the federal government and other states. This has resulted in a unique list of items that are banned for sale within the state due to environmental or health concerns, yet remain available elsewhere in the U.S. Here are 14 such items, providing insights into why they are deemed dangerous and the contrast between California’s laws and those of other states.

1. Certain Types of Pesticides

California has banned the sale and use of specific pesticides that contain chemicals known to be particularly harmful to the environment and human health. These include neonicotinoids, which have been linked to bee population declines and are still available in many other states. While these pesticides are effective at controlling pests, their long-term impacts on pollinators, which are crucial for the pollination of many crops, have prompted California to prohibit their use to protect its diverse ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
California’s stance on pesticides makes sense given the massive size of the agriculture industry in the state. In 2023 the state’s agricultural exports were valued at over $23 billion dollars. This means crops and crop safety are a high priority for California governance.
2. Non-OBD Compliant Vehicles

On-board diagnostics (OBD) systems help monitor the performance of a vehicle’s engine and other essential systems. Since 1988 California requires all vehicles to be OBD-compliant to ensure they meet specific emissions standards. Non-compliant vehicles, which can be sold in other states, often fail these stringent environmental checks.
By prohibiting the sale of non-OBD compliant vehicles, California aims to reduce air pollution and promote public health. While California has some of the toughest OBD standards in the nation, the state is home to millions of cars which drive at ever increasing rates. This means auto emissions are the single greatest source of smog forming emissions in the state (Per the California Air Resources Board).
3. Certain Flame Retardants in Furniture and Children’s Products

California bans the use of certain flame retardants in furniture and children’s products due to studies showing potential links to cancer and developmental problems in children (here). These chemicals are still used in products sold in other parts of the country. The state’s proactive approach to banning these substances highlights a significant discrepancy in consumer safety laws across the U.S., where other states lag in implementing similar protections.
4. Single Use Plastic Bags

Using a series of laws enacted between 2014 and 2024 California outlawed single-use plastic bags (NPR news). This is due to their harmful environmental impact, notably in oceans and on wildlife. Other states continue to allow these bags to be distributed freely at retail locations. While some argue that plastic bags are convenient, California’s ban reflects a broader commitment to reducing waste and protecting marine life, which has not been universally adopted in other states.
5. Certain Beauty Products Containing Toxic Substances

California has specific regulations against some beauty products that contain ingredients like formaldehyde and certain parabens and phthalates, which are linked to health risks. These products remain accessible in other U.S. markets. These regulations are part of preventive measures in the California 2005 Safe Cosmetics Act. The act aims to protect consumers from exposure to toxic substances through everyday beauty products—a comprehensive regulation not as prevalent in other states.
6. Lead-Based Ammunition

As of July 1st, 2019, nonlead ammunition is required when taking any game animal in California. This ban on lead-based ammunition is intended to protect the environment from the harmful effects of lead. In contrast to California, this type of ammunition is still widely available in other states. The continued use of lead bullets in other states poses significant environmental and health risks, highlighting a critical area of public policy where California is a standout.
7. Fluorescent Light Bulbs

California has phased out the sale of less energy-efficient fluorescent light bulbs to promote the use of more sustainable alternatives like LED bulbs. This shift is part of California’s broader strategy to combat climate change, whereas other states still sell traditional bulbs. Switching to LEDs not only reduces energy consumption but also lowers electricity bills for consumers, demonstrating an area where economic and environmental benefits align.
8. Foie foie gras
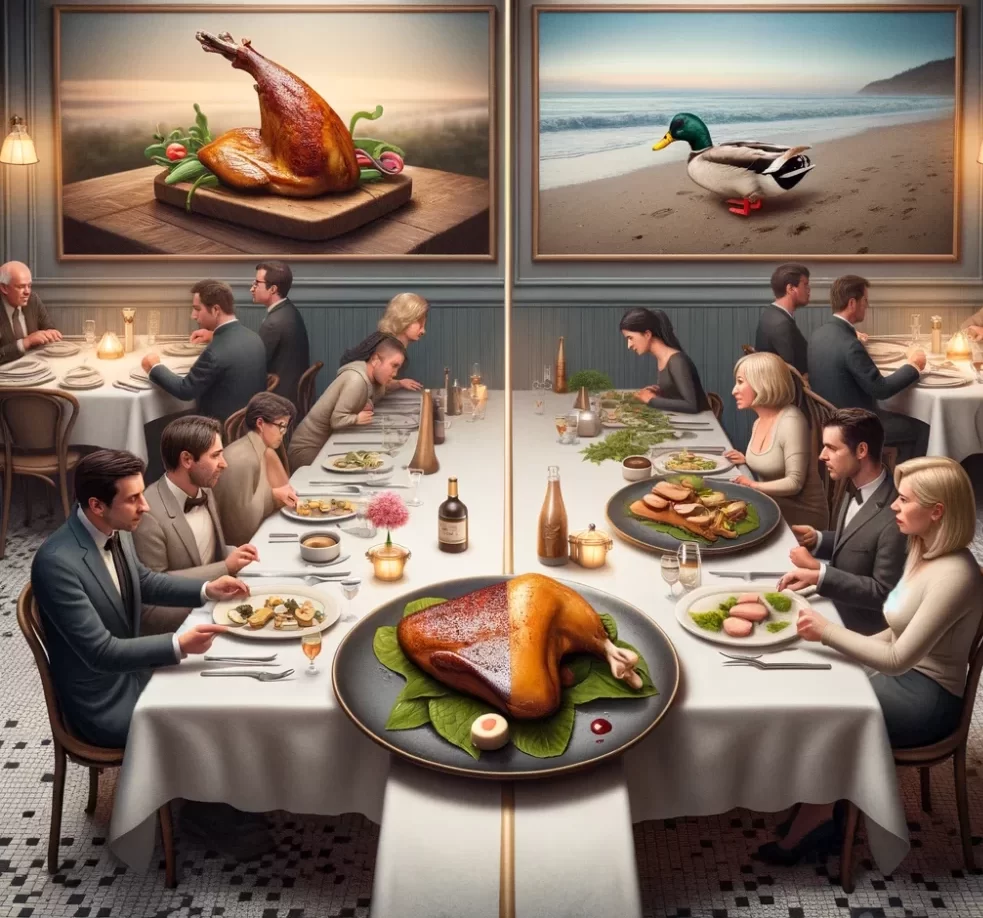
Due to animal welfare concerns, California has banned the sale of foie gras, a delicacy produced from the liver of ducks or geese that have been force-fed (see Wikipedia for a summary of the ongoing wrangling over the ban). Other states do not have such bans, allowing the continued sale and consumption of foie gras. The ban reflects a growing trend toward more humane treatment of animals in food production, which has sparked significant debate on culinary practices and animal rights across the nation.
9. Certain Types of Fishing Gear

In an effort to protect marine life, California prohibits the use of certain types of fishing gear that are known to cause significant bycatch, such as gill nets. These practices are still permitted in many other states, where they continue to affect marine biodiversity adversely. California’s regulations aim to promote sustainable fishing practices that help maintain the health of marine ecosystems, contrasting with less stringent regulations elsewhere.
10. High-Capacity Magazines for Firearms

High-capacity magazines that hold more than ten rounds are banned in California due to concerns about their use in mass shootings. Other states, however, continue to permit the sale and possession of these items. The ban is part of California’s approach to gun control, designed to reduce access to firearms and related equipment in an attempt to lessen the potential for gun violence, reflecting a policy divide in the United States.
11. Aftermarket Exhaust Systems

California restricts the use of certain aftermarket exhaust systems on vehicles because they can significantly increase noise levels and emissions. These systems are still popular and legal in other parts of the country where regulations may be less strict. The state’s stance on these modifications aligns with its broader environmental and public health goals, aiming to reduce noise pollution and improve air quality.
The specialty auto parts industry has a good summary of California’s restrictions at their website.
12. Certain Herbicides

Herbicides containing glyphosate, a chemical linked to cancer, are restricted in California. In contrast, these herbicides are widely available and used across other states in the U.S. California’s regulatory measures reflect its proactive approach to public health and environmental protection, often leading to stricter standards than those found federally or in other states.
13. Shark Fins
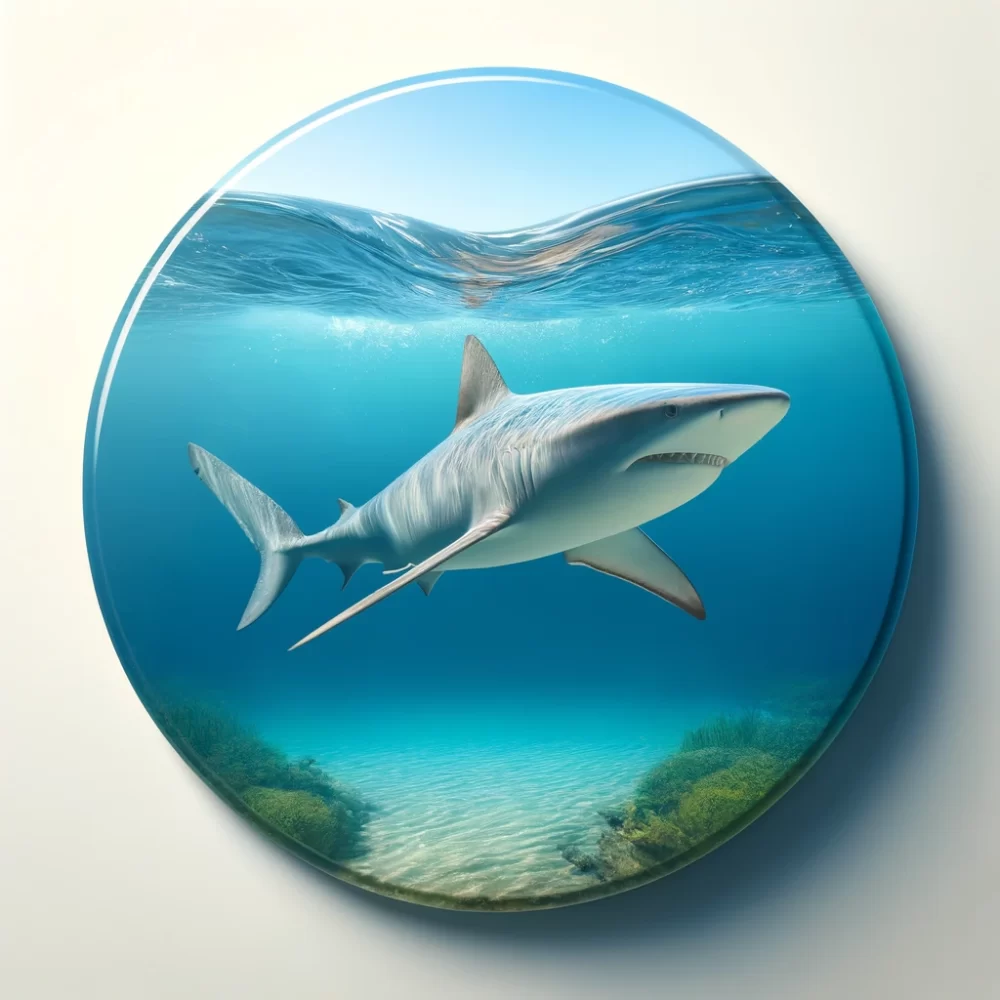

In 2011 California Governor Brown signed AB 376 into law. AB 376 made it illegal to sell, trade, possess, or distribute shark fins within the state of California. This ban is part of the states efforts to discourage shark finning, a practice that threatens shark populations and disrupts marine ecosystems. This ban is not enforced in many other states, where the market for shark fins continues. California’s ban is an example of its leadership in marine conservation and reflects broader environmental values that may not be as prevalent in other regions.
14. Bisphenol A (BPA) in Baby Products

Through a series of laws and regulatory actions, California severely restricts the use of Bisphenol A (BPA) in baby bottles and other products for infants due to concerns over its potential effects on child development. BPA is a compound used in the manufacturing of plastics such as food containers and water bottles (here), and is still found in some baby products sold outside of California. This regulation is part of California’s commitment to safeguarding children’s health, highlighting differences in consumer protection laws across the country.
15. Junk Food in Schools
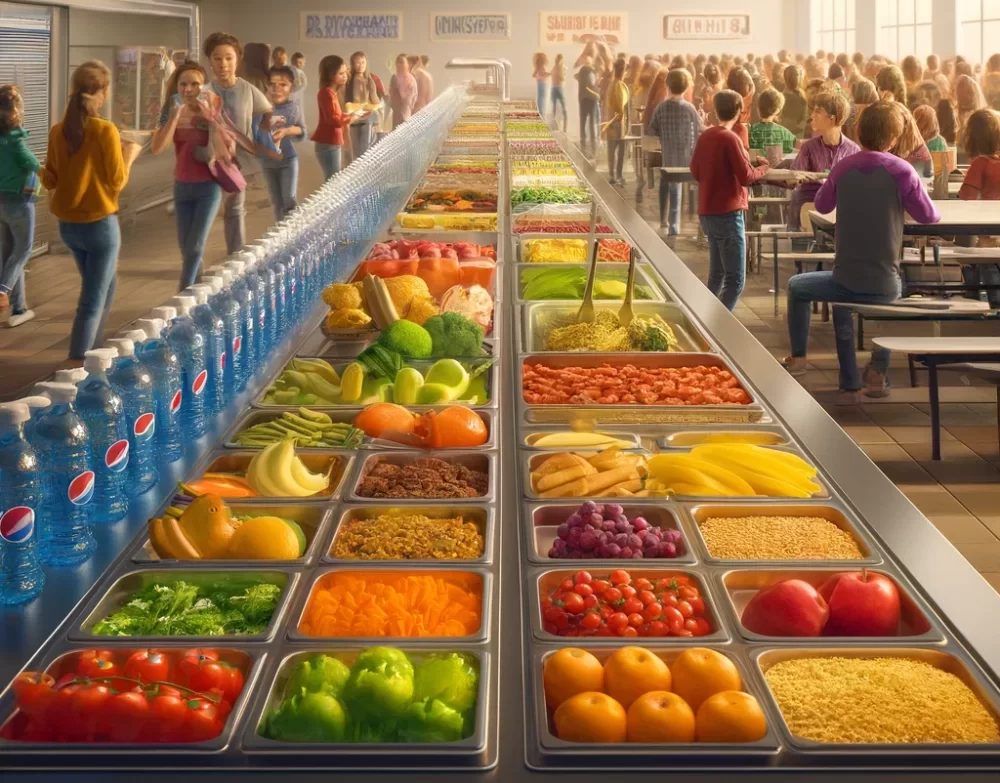

In an attempt to combat childhood obesity, California has passed a number of laws banning the sale of certain types of junk food in public schoolsincluding soda and candy. Other states have yet to implement such stringent standards. California’s initiative aims to promote healthier eating habits among students and address public health concerns. And, according to the New York Times, this effort appears to have paid off in the form of lower calorie consumption in California schools – and in amounts significant enough to prevent or lessen childhood obesity (The Times, Here).
Is California’s Approach Always Best?
California has been heavily criticized for having “nanny state” style governance. Critics of California’s policies point to the states recent high crime rate, traffic, failures of local governance during the recent fires in Los Angeles, as well high taxes and regulatory burden. Critics also note that California has recently experienced a surge of business migration away from the state towards States like Texas (Wikipedia).
So, although California has passed several laws that are well ahead of the rest of the nation, its not clear that the approach taken by California’s legislators is always best.




GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings